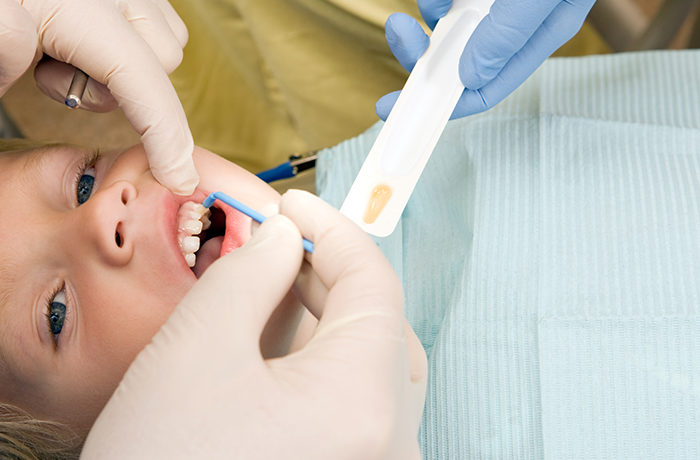
Educational
Educational is a prescription antibiotic approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). It is used together with scaling and root planing (SRP) and is placed by your dentist for the treatment of periodontal (gum) disease.Educational contains microspheres (tiny particles) that are smaller than grains of sand and are not visible to the eye. The microspheres are filled with the antibiotic minocycline hydrochloride. These microspheres release the antibiotic over time, killing bacteria so your gums can heal better than with SRP alone.
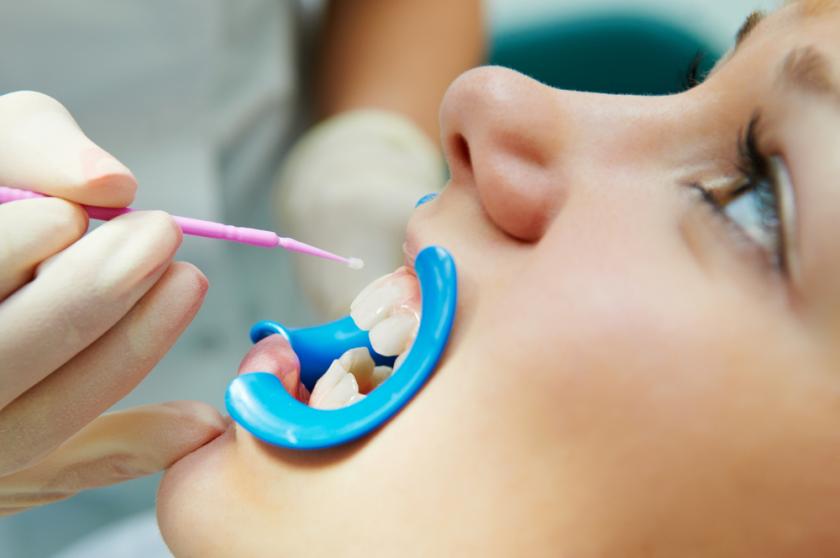
Sealants
Dental sealants are thin plastic coatings that are applied to the grooves on the chewing surfaces of the back teeth to protect them from tooth decay. They protect the chewing surfaces from tooth decay by keeping germs and food particles out of these grooves.
Permanent molars are the most likely to benefit from sealants. The process is short and easy. After the tooth is cleaned, a special gel is placed on the chewing surface for a few seconds. The tooth is then washed off and dried. Then, the sealant is painted on the tooth. The dentist or dental hygienist also may shine a light on the tooth to help harden the sealant. It takes about a minute to form a protective shield.
Sealants can only be seen up close; they can be clear, white, or slightly tinted. A sealant can last for as long as 5 to 10 years. Sealants should be checked at each regular dental appointment and can be reapplied if they are no longer in place.
Periodontal Cleanings
Periodontal cleaning is part of oral hygiene and involves the removal of dental plaque from teeth with the intention of preventing cavities, gingivitis and periodontal disease. People routinely clean their own teeth by brushing and dental hygienists can remove hardened deposits (tartar) not removed by routine cleaning. Prior to this type of treatment, your dentist will apply a local anesthetic.
Scaling and Root Planing
Scaling and root planing is the process of removing or eliminating the etiologic agents – dental plaque, its products, and calculus – which cause inflammation, thus helping to establish areas around the teeth that are free of disease.
Periodontal scaling procedures include the removal of plaque, calculus and stain from the crown and root surfaces of teeth. Root planing is a specialized skill involving scaling of the root of the tooth, made up of cementum. Since cementum is softer than enamel, it is affected more by ongoing build-up and inflammatory byproducts. A smooth cementum provides less opportunity for bacteria to accumulate and form calculus. So root planing is an important part of stopping the progression of periodontal disease, especially once deeper pockets have formed in the gums.